The next time you are out shopping at a grocery or retail store, you may encounter a robot roaming around the floor. But what are these in store robots doing? In this post, we explain exactly what robots in stores are up to and how they work!


Floor Cleaning Robots
These machines are in charge of cleaning the floors, removing dirt and absorbing spills. Most major stores will run these machines at night when the store is closed. This keeps the store clean and also keeps the floor safe and smooth. Similar to roads, small holes in the floors can appear if not properly maintained. The lifespan of the floor is lengthened when proper floorcare is followed. We can compare previous human floor cleaning to the robot equivalent below:




The robots either learn or follow pretrained paths in the store, and clean the floors while avoiding obstacles like shoppers or shelves.
Inventory Counting (Shelf Scanning) Robots
One part of a retail employees tasks is often maintaining an accurate inventory count. This helps determine what to order / stock from the backroom. Today, this is done manually by a store associate, taking their valuable time away from cash register or restocking / helping customers. You can see the comparison between human and robot inventory counting (shelf scanning) below:




As the robot drives past the shelves, it scans and processes images to determine “out of stock” products and if price tags have not been properly updated.
How do robots in retail stores work?
Robots rely on sensors to help the robot “see” the environment to avoid driving into things when moving autonomously. A variety of sensors are combined to “see” different parts of the environment at once:


For more information on how sensors work, check out our post on how robots experience the world. Additionally, the robots rely on their autonomy system to navigate the store by themselves. This includes:
- Perception (what is around me?)
- Localization (where am I?)
- Motion Planning (where should I go?)
Together, these features make up robot “brains” that let it move. Notice in the example below, the top right 2D representaiton of the world is how the robot determines where it can go, based on where its sensors have seen obstacles or free space:
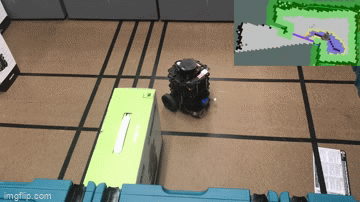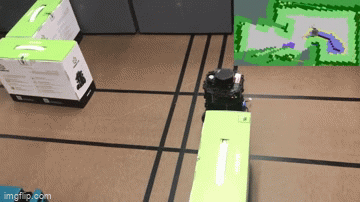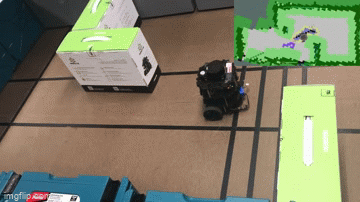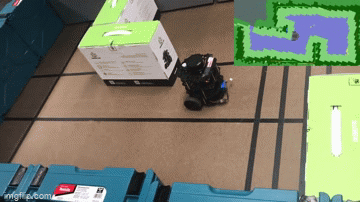

Finally, for behaviors such as inventory counting or shelf scanning, the robot relies on computer vision and cameras to take pictures and analyze them to determine if a given product is out of stock on a shelf or if the price tag is not updated correctly:


If you want to learn more about how robots see, check out our post on computer vision and how robots see.
Will we see more robots in retail?
As labor costs continue to rise due to labor shortages, retailers are looking towards robotics and automation to make their staff more productive. We can see robotics is a growing industry, with more spent on robotics and more robots being used in the world year over year:
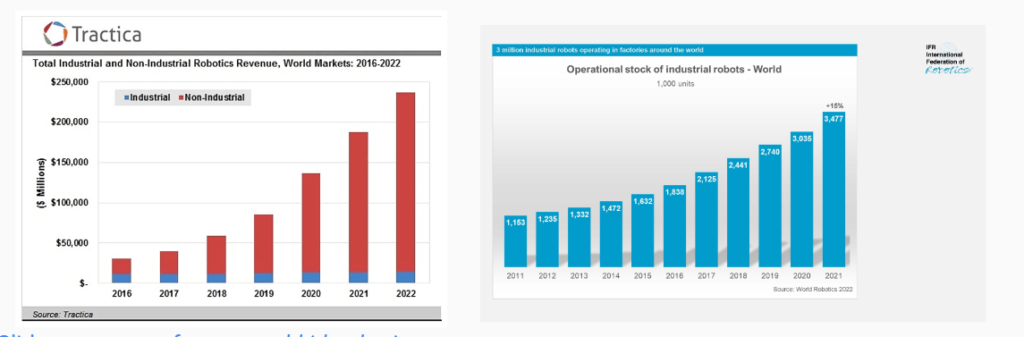

In a recent survey conducted by RetailWire and Brain Corp, 64% of retailers believe it is important to have a clear, executable, and budgeted robotics automation strategy in place in 2021.
If you want to learn more about robots, start our series with our post on what is a robot?